When people learn about hereditary breast and ovarian cancer, one of the first BRCA 1 vs BRCA 2; what’s the real difference in cancer risk and why does it matter?
Understanding BRCA 1 vs BRCA 2 is important not only for families with a history of cancer but also for anyone who wants clarity about genetic risk, prevention, and personalised healthcare decisions.
Through this we will answer the question of what the BRCA gene is, discuss what the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are, and explain the difference in relation to cancer risk, age of onset, along with overall health outcomes.
Let’s start.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is the BRCA gene?
Before comparing BRCA 1 vs BRCA 2, it is essential to first understand what is the BRCA gene and why it plays such a critical role in cancer prevention.
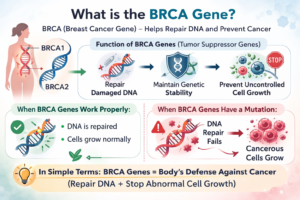
BRCA is an acronym that stands for breast cancer gene. There are two main BRCA genes in the human body, namely BRCA1 and BRCA2. These genes are tumor suppressor genes. This means that the job of these genes is to:
- Repair damaged DNA
- Ensure that the genetic makeup of the body remains stable
- Prevent cells from growing and dividing in an uncontrolled manner
In other words, the BRCA genes are like the body’s immune system against cancer. When they are working as they should, they help to repair errors in the DNA that occur naturally with time.
But when a mutation (a deleterious change) occurs in either the BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene, the gene is not able to repair the DNA properly. This leads to the possibility of cancerous cells growing.
So, in simple terms, if you are wondering what the BRCA gene is, it is a protective gene responsible for repairing DNA and preventing abnormal cell growth.
BRCA1 and BRCA2 Genes
Now that we understand what is the BRCA gene, let’s clearly answer another common question; what is BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, and how do they function individually?
BRCA1 and BRCA2 are inherited genes. When people ask about BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, the simple answer is that they are tumour-suppressing genes passed down from parents that help repair damaged DNA and reduce cancer risk.
Each individual has two genes of every type, one from each parent. If one gene has a mutation, then the individual faces an increased lifetime risk of certain cancers.
BRCA1 Gene
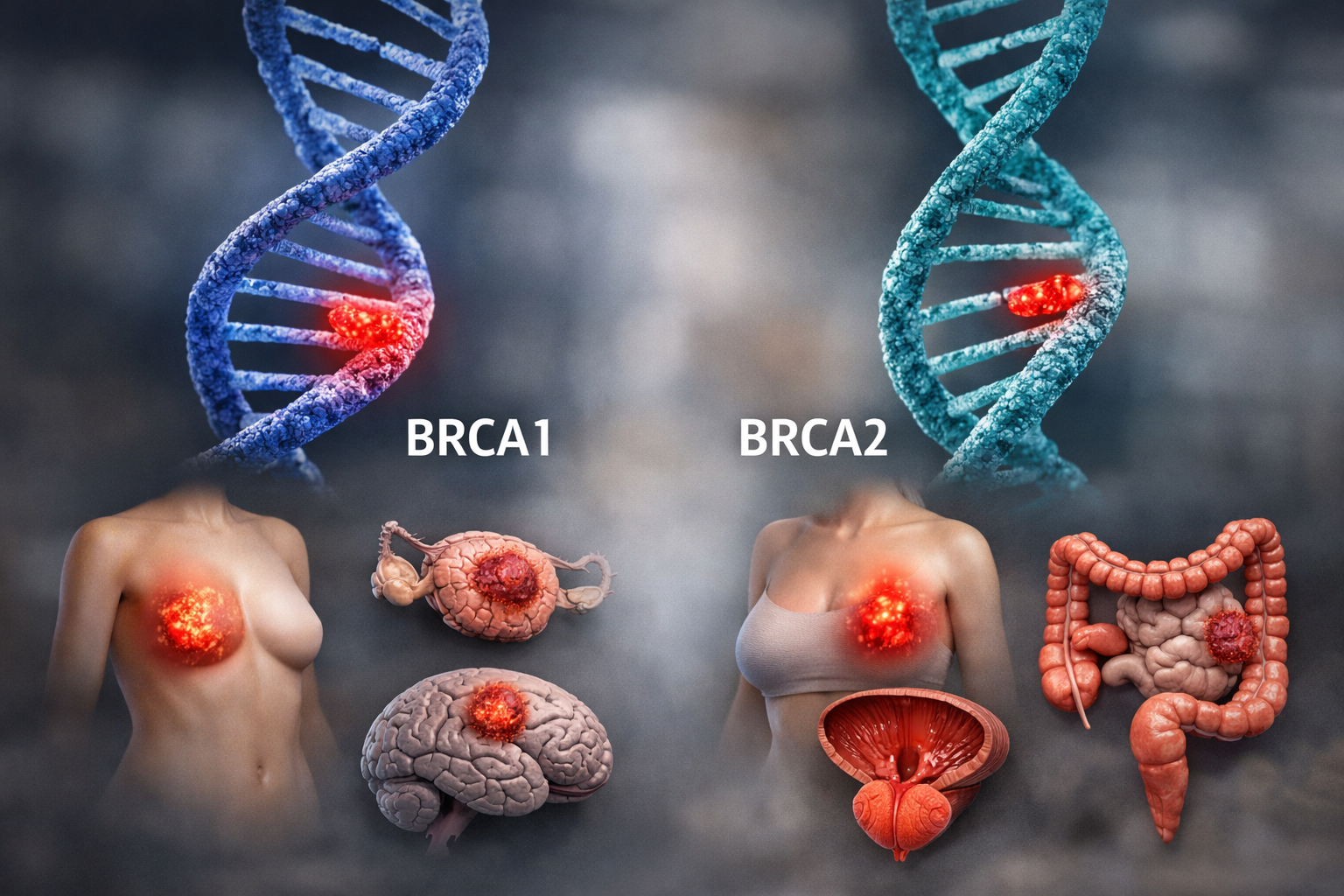
BRCA1 gene mutations are known to significantly increase the risk of:
- Breast cancer
- Ovarian cancer
- Fallopian tube cancer
- Triple-negative breast cancer
- Pancreatic cancer
BRCA1-linked breast cancers are more likely to be aggressive and occur at a younger age.
BRCA2 Gene
BRCA2 gene mutations are also known to increase the risk of certain cancers, including:
- Breast cancer (in women and men)
- Ovarian cancer
- Prostate cancer
- Pancreatic cancer
- Melanoma
Women with BRCA2 mutations face a lifetime risk of breast cancer between 45% and 69%. The risk of ovarian cancer is generally lower than BRCA1, at 11% to 17%.
Men with BRCA2 mutations face a significantly increased lifetime risk of male breast cancer and prostate cancer.
Difference Between BRCA1 and BRCA2
When looking at what is difference between BRCA1 and BRCA2?
They are different in relation to the type of cancer, age of onset, and cancer characteristics.
-
Breast Cancer Risk
Both genes significantly increase the risk of breast cancer, but:
BRCA1 is more often linked to triple-negative breast cancer, which is more aggressive and difficult to treat.
Breast cancers due to BRCA2 are more likely to be hormone receptor-positive, meaning they are more likely to be treated with hormone therapy.
-
Ovarian Cancer Risk
The risk of ovarian cancer due to BRCA1 mutations is higher than that of BRCA2.
Ovarian cancers due to BRCA1 mutations occur at a younger age.
-
Male Cancer Risk
BRCA2 is more strongly linked to male breast cancer and prostate cancer.
BRCA1 also increases the risk of cancer in men, but to a lesser extent.
-
Age of Onset
Cancers linked to BRCA1 tend to occur at a younger age.
Cancers associated with BRCA2 tend to occur a little later in life.
-
Tumor Behavior
Cancers linked to BRCA1 are more likely to be aggressive and grow quickly.
Cancers associated with BRCA2 may respond better to treatment because they are hormone receptor-positive.
It is essential to recognize these differences to create personalized screening and prevention plans.
Who Should Consider BRCA Testing?
After understanding BRCA 1 vs BRCA 2 and their associated risks, many people wonder whether they should undergo genetic testing.

So, genetic testing is advised if you have:
- A family history of breast or ovarian cancer
- A first-degree relative with breast cancer before age 50
- Male breast cancer in the family
- Several family members with related cancers
- A known BRCA mutation in a first-degree relative
Testing is usually done by blood or saliva sample. If a mutation is discovered, your doctors can offer you increased screening, preventive medications, or even risk-reducing surgery.
Emotional and Lifestyle Impact of BRCA Mutations
It’s understandable that receiving the news of a BRCA mutation can be stressful. In addition to the health implications, the individual may be concerned about:
- Cancer occurrence
- Decisions concerning preventive mastectomy or oophorectomy
- Family planning
- Discussing the condition with family members
It’s also important to note that being aware of the mutation can be empowering. Early detection and preventive care can greatly impact the outcome.
In discussing the differences between BRCA 1 and BRCA 2, the key factor is not to instill fear but to be aware and manage one’s healthcare.
Advances in Research and Precision Medicine
Medical studies are also improving the management of cancers related to BRCA mutations. For instance, studies on PARP inhibitors indicate that they are effective in treating patients with BRCA mutations.
Precision medicine is improving, enabling individuals to get treatment that is customized to their genetic makeup. Advances in technology are improving the management of cancer, and we are getting closer to more effective means of preventing cancer.
The Role of Technology in Genetic Risk Awareness
Today, we are living in a digital age, and technology is playing a critical role in improving the accessibility of genetic education and healthcare technologies.
Businesses that develop digital health technologies, artificial intelligence-based diagnostic tools, and secure medical software applications are changing the way people understand genetic conditions such as BRCA mutations.
Uncoded develops innovative digital technologies that can simplify complex medical information, improving patient engagement.
It has been helping organizations develop healthcare software solutions that can make genetic information more accessible, understandable, and actionable.
Prevention and Risk Management Strategies
If an individual has a BRCA mutation, the management of risk can be done through:
- Early and more frequent mammograms
- Annual breast MRI scans
- Preventive drugs
- Changes to one’s lifestyle
- Preventive surgery, especially for those who are considered high-risk patients
A healthy lifestyle, including eating a balanced diet, abstaining from alcohol, exercising regularly, and not smoking, can also play a part in reducing cancer risk.
Final Thoughts
If you are still asking what is BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, they are essential tumour-suppressor genes that protect the body from becoming cancer when functioning normally.
And when comparing BRCA 1 vs BRCA 2, the key differences lie in cancer type, seriousness, age of onset, and the level of risk, especially for ovarian, prostate, and male breast cancer.
Genetic knowledge is not about fear; it is about preparation, prevention, and empowerment. As healthcare technologies continue to advance with the development of new technologies by Uncoded, more opportunities for individuals to understand their genetic risks exist.