In today’s world of oncology and precision medicine, genetic testing is changing the face of cancer detection and treatment. One of the biggest advancements that has come out of this field is the discovery of how to detect homologous recombination deficiency (HRD), which is a deficiency within the body that causes it to be unable to repair damaged DNA.
Knowing what is HRD testing, how HRD genetic testing works, and why deficiency testing is important can help individuals make more informed decisions about their cancer treatment.
As medical technology continues to improve, HRR (Homologous Recombination Repair) testing is proving to be an important factor in cancer treatment.
Let’s discuss the details through this blog.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding DNA Repair and Homologous Recombination
Regularly our cells are subjected to thousands of DNA breaks because of our metabolism, the environment we are exposed to, and even DNA replication errors. The good news is that our bodies are designed with DNA repair systems to correct these errors.
Homologous recombination repair (HRR) is one of the most accurate DNA repair systems that:
- Repairs double-strand DNA breaks
- Uses an intact DNA template to repair the broken DNA
- Maintains genome stability
When the HRR system is functioning properly, it prevents the occurrence of mutations. When the system fails, it results in homologous recombination deficiency, which may lead to the development of cancer.
What Is Homologous Recombination Deficiency?
Homologous recombination deficiency is the result of HRR pathway impairment. This impairment results from mutations in particular genes, such as
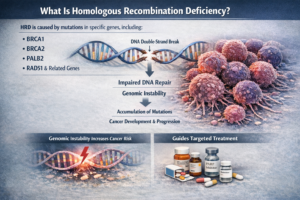
- BRCA1
- BRCA2
- PALB2
- RAD51 and related genes
When these genes are mutated, the cell is not able to repair DNA double-strand breaks properly. Instead, the cell uses inaccurate repair methods, causing genomic instability.
Genomic instability is one of the defining features of cancer. Cells with DNA repair defects accumulate mutations over time, which may result in the development and progression of cancer.
Homologous recombination deficiency is important because not only does it provide an explanation for the development of certain cancers, but it also indicates the appropriate treatment methods.
Overview of HRD Testing
The most common question asked by patients is, What is HRD testing?
HRD testing is a specific type of genomic testing that analyzes if there is a defect in the homologous recombination repair mechanism of the tumor. Instead of testing one specific gene, HRD testing analyzes many different markers that point to a defect in DNA repair.
In essence, HRD testing is a genetic test that detects if cancer cells cannot repair their DNA.
- The testing can include the following factors:
- Mutations in the BRCA1/2 genes
- Genomic instability scores
- Loss of heterozygosity
- Telomeric allelic imbalance
- Large-scale state transitions
This allows doctors to determine if the tumor is HRD positive or HRD negative.
How HRR Testing Identifies DNA Repair Deficiencies
Homologous Recombination Deficiency testing essentially involves the following process:
- Sample Collection: A Tumor tissue sample or blood sample is collected.
- Genomic Sequencing: The DNA is then analyzed to look for mutations or changes.
- Biomarker Analysis: Specific biomarkers of homologous recombination deficiency are measured.
- HRD Score Calculation: The genomic instability score is used to determine if the tumor has homologous recombination deficiency.
- Classification: If the score is above a specific threshold, then the tumor is classified as HRD-positive.
This classification is important because HRD-positive tumors can respond favorably to therapy with PARP inhibitors.
Why HRD Genetic Testing Matters in Cancer Treatment
The importance of HRD genetic testing is its ability to inform precision medicine.

- Personalized treatment decisions
Patients who have homologous recombination deficiency have a greater chance of responding to the following treatments:
- PARP Inhibitors
- Platinum Chemotherapy
- Targeted therapies for tumors deficient in DNA repair
These treatments target the cancer cells’ inability to repair their DNA, resulting in the death of the cancer cells.
- Expanded patient eligibility
In the past, treatment decisions have only been available to patients who have a BRCA mutation.
However, HRD genetic testing extends the treatment eligibility to other patients who have a chance of responding to targeted therapy, even though they do not have a BRCA mutation.
- Better prognostic understanding
In addition, HRD status offers important prognostic information to help oncologists develop effective treatment plans.
Cancers Most Commonly Associated with HRD
Homologous recombination deficiency is most commonly associated with the following cancers:
- Ovarian Cancer
- Breast Cancer
- Prostate Cancer
- Pancreatic Cancer
The Science Behind Synthetic Lethality
One of the most powerful concepts related to homologous recombination deficiency is synthetic lethality.
If the tumor already has a defective HRR pathway, then inhibiting an alternative repair pathway (such as PARP) overwhelms the ability of the cancer cell to survive. This has less of an impact on normal cells, which still have intact HRR pathways.
Thus, PARP inhibitors are particularly effective in HRD-positive cancers. Knowing more about what HRD testing is can help patients understand the relevance of this scientific concept to their care.
The Role of Technology in HRD Testing
HRD genetic tests heavily depend on the use of cutting-edge genomic sequencing technologies. This has, therefore, created a need for the use of cutting-edge digital technologies. This is where technology companies come in.
Uncoded is one of the technology companies that develop intelligent digital solutions. It has been established with the aim of simplifying complex healthcare data systems. It achieves this through the development of cutting-edge software platforms like HRR Panel.
As the need for homologous recombination deficiency tests continues to grow, technology-driven innovation remains critical. This is because technology ensures that results are obtained accurately.
Who Should Consider HRD Genetic Testing?
Doctors may suggest HRD genetic testing in cases of:
- Patients with diagnosed ovarian cancer
- Patients with advanced-stage breast cancer
- Patients with prostate cancer or pancreatic cancer
- Patients with a family history of cancer related to BRCA
The test may especially be useful in deciding whether to opt for a targeted therapy. It is important to note that HRD testing is conducted on tumor tissue, but germline testing looks at inherited mutations.
Benefits and Limitations of Homologous Recombination Deficiency Testing
Benefits
- Identifies patients who can benefit from targeted treatment
- Moves beyond BRCA testing
- Enhances personalized medicine
- Offers predictive treatment clues
Limitations
- Thresholds for testing may vary
- Interpretation of results requires expertise
- Not all HRD-positive cancers respond equally well
In spite of the challenges, homologous recombination deficiency testing is an important tool in today’s oncology practice.
The Future of HRR Testing in Precision Medicine
As medical science continues to evolve, HRR tests are likely to become an integral part of the diagnosis and treatment of cancers. The next steps in the field involve
- Development and enhancement of HRD scoring systems
- Expanding HRR tests to cover different types of cancers
- Development and enhancement of predictive biomarkers
- The integration of artificial intelligence in the field
- The future of oncology is all about precision-based treatment strategies.
As the availability and ease of access to genetic tests increase with the development and implementation of better digital tools by innovative companies such as Uncoded, patients stand to benefit from the diagnosis and treatment process.
Final Thoughts
Homologous recombination deficiency is a vital factor in the development, behavior, and treatment of some types of cancer. By identifying weaknesses in the DNA repair mechanism, homologous recombination deficiency testing can provide important information about a tumor’s characteristics, which can greatly influence treatment decisions.
Learning what is HRD testing and how HRD genetic testing works can enable both cancer patients and healthcare professionals to go beyond the generic treatment approach and move toward precision medicine.
Homologous recombination deficiency testing not only extends treatment options beyond the more commonly known BRCA mutations but also increases the likelihood of matching cancer patients with treatment options that can greatly increase treatment effectiveness.
As science in the field of genomics continues to advance and new technologies in digital health continue to evolve with the support of forward-thinking innovators in the tech industry, such as Uncoded, the future of cancer treatment is looking more promising.

